Alles, was Sie über Aluminiumoxidkeramik wissen müssen
Was ist Aluminiumoxidkeramik?
Aluminiumoxidkeramik ist ein hochentwickelter technischer Keramikwerkstoff, der hauptsächlich aus Aluminiumoxid (Al₂O₃) besteht.
Aufgrund seiner ausgezeichneten elektrischen Isolationsfähigkeit, hohen Härte, guten Verschleißfestigkeit und chemischen Stabilität ist es eines der am weitesten verbreiteten keramischen Werkstoffe in industriellen, elektrischen und mechanischen Anwendungen.
Aufgrund seiner ausgewogenen Eigenschaften und der vergleichsweise ausgereiften Herstellungsverfahren wird Aluminiumoxidkeramik bei der Auswahl technischer Keramik für industrielle Bauteile oft als Basismaterial betrachtet.
Chemische Zusammensetzung und Mikrostruktur von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
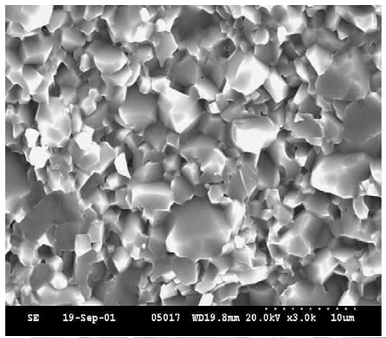
Die Leistungsfähigkeit von Aluminiumoxidkeramik wird in erster Linie durch ihre chemische Zusammensetzung und Mikrostruktur bestimmt.
Chemisch gesehen bestehen Aluminiumoxidkeramiken hauptsächlich aus Aluminiumoxid (Al₂O₃), wobei der genaue Reinheitsgrad das elektrische, thermische und chemische Verhalten beeinflusst.
Aus mikrostruktureller Sicht spielen Faktoren wie Korngröße, Dichte und Restporosität eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Bestimmung der mechanischen Festigkeit, der dielektrischen Eigenschaften und der Langzeitstabilität.
Daher können Aluminiumoxidkeramiken mit ähnlicher chemischer Zusammensetzung je nach Rohmaterialqualität und Verarbeitungsbedingungen deutlich unterschiedliche Eigenschaften aufweisen.
Haupteigenschaften von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
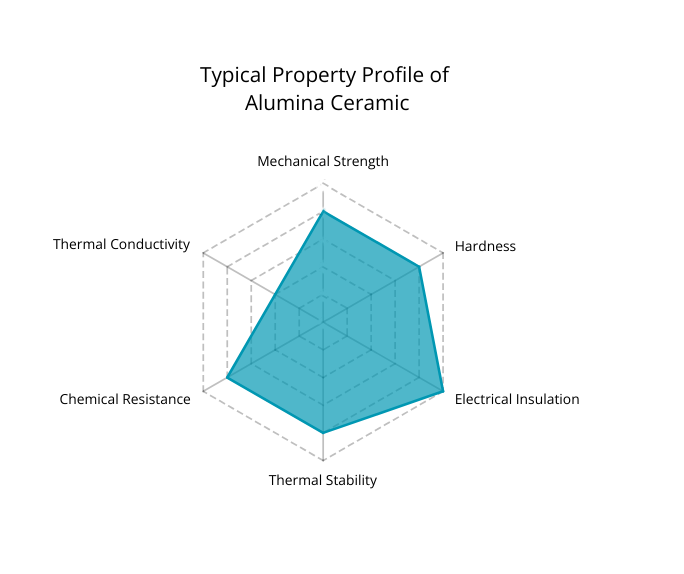
Mechanisches Schließenrties
Aluminiumoxidkeramik ist bekannt für ihre hohe Härte und gute Verschleißfestigkeit und eignet sich daher für Bauteile, die Reibung und abrasiven Umgebungen ausgesetzt sind. Typische Biegefestigkeits- und Härtewerte variieren je nach Reinheit und Herstellungsverfahren, jedoch bieten Aluminiumoxidkeramiken im Allgemeinen eine zuverlässige mechanische Stabilität für industrielle Anwendungen.
Wie die meisten Oxidkeramiken ist Aluminiumoxid von Natur aus spröde, was bedeutet, dass es nur eine begrenzte Toleranz gegenüber Stoßbelastungen oder Zugspannungen aufweist. Konstruktionsaspekte wie Geometrieoptimierung und korrekte Montage sind daher wichtig.mechanische Festigkeit von Aluminiumoxidkeramikwird oft missverstanden, insbesondere bei der Bewertung anhand von Kriterien, die für Metalle entwickelt wurden. Konstruktionsaspekte wie Geometrieoptimierung und sachgemäße Montage sind daher wichtig.
👉Wie fest ist Aluminiumoxidkeramik?
Elektrische Eigenschaften
Eine der wichtigsten Eigenschaften von Aluminiumoxidkeramik ist ihre ausgezeichnete elektrische Isolationsfähigkeit.
Es weist eine hohe Durchschlagsfestigkeit und ein stabiles Isolationsverhalten über einen weiten Temperaturbereich auf, was seine breite Anwendung in elektrischen und elektronischen Bauteilen erklärt. Dielektrische Eigenschaften wie Dielektrizitätskonstante und Verlustfaktor können mit Reinheit, Frequenz und Temperatur variieren und werden daher häufig bei der Materialauswahl für elektronische Anwendungen berücksichtigt.
👉Elektrische Isolationseigenschaften von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
Thermische Eigenschaften
Aluminiumoxidkeramik bietet eine gute thermische Stabilität und kann bei erhöhten Temperaturen dauerhaft betrieben werden.
Seine Wärmeleitfähigkeit ist im Vergleich zu anderen technischen Keramiken moderat und sorgt in vielen Anwendungen für eine ausreichende Wärmeableitung. Allerdings ist es nicht für Hochleistungs-Wärmemanagementanwendungen gedacht, bei denen Materialien wie Aluminiumnitrid bevorzugt werden.
Die Temperaturwechselbeständigkeit von Aluminiumoxidkeramik ist für kontrollierte thermische Umgebungen im Allgemeinen akzeptabel, jedoch geringer als die von Nichtoxidkeramiken wie Siliziumnitrid.
Chemische Stabilität
Aluminiumoxidkeramik weist in vielen industriellen Umgebungen eine ausgezeichnete Beständigkeit gegenüber Korrosion und chemischen Angriffen auf. Sie bleibt in Gegenwart der meisten Säuren und Laugen bei Raumtemperatur stabil und wird häufig unter chemisch aggressiven Betriebsbedingungen eingesetzt.
Reinheitsgrade von Aluminiumoxidkeramik und ihre industrielle Bedeutung
In industriellen Anwendungen werden Aluminiumoxidkeramiken mit unterschiedlichen Eigenschaften hergestellt.Aluminiumoxid (Al₂O₃)-GehaltDie Materialien werden so ausgewählt, dass sie den Leistungsanforderungen spezifischer Betriebsbedingungen gerecht werden. In der Praxis werden Materialspezifikationen durch explizite Reinheitswerte definiert, da diese die zuverlässigste Grundlage für Konstruktion und Qualitätskontrolle bieten.
Aus ingenieurtechnischer Sicht beeinflusst die Reinheit von Aluminiumoxid Eigenschaften wie die Stabilität der elektrischen Isolation, die chemische Beständigkeit, die mikrostrukturelle Konsistenz und die Langzeitstabilität. Eine höhere Reinheit führt jedoch nicht zwangsläufig zu einer besseren Gesamtleistung, insbesondere wenn mechanische Belastung, thermische Gradienten oder Kostenbeschränkungen primäre Konstruktionskriterien darstellen.
👉Leitfaden für Aluminiumoxid-Keramikqualitäten: Auswahl zwischen 95 % und 99,8 % Reinheit
Herstellung und Verarbeitung von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
Aluminiumoxid-Keramikbauteile können mithilfe verschiedener Formgebungs- und Verarbeitungsverfahren hergestellt werden, die je nach Bauteilgeometrie, Leistungsanforderungen und Produktionsumfang ausgewählt werden.
Gängige industrielle Verfahren umfassen Pressverfahren, Gießverfahren und Extrusions- oder Bandformtechniken, die jeweils unterschiedliche Vorteile in Bezug auf Maßhaltigkeit, Dichtekontrolle und Oberflächengüte bieten.
Nach der Formgebung werden die Aluminiumoxid-Keramikteile einem Hochtemperatur-Sinterprozess unterzogen, bei dem es zu einer Verdichtung und einer Dimensionsschrumpfung kommt.
Für Anwendungen, die enge Toleranzen oder spezielle Oberflächenbeschaffenheiten erfordern, werden häufig sekundäre Bearbeitungsprozesse wie Schleifen oder Läppen eingesetzt.
Die Wahl des Herstellungsverfahrens hat einen wesentlichen Einfluss auf die endgültigen mechanischen, elektrischen und dimensionalen Eigenschaften von Aluminiumoxid-Keramikbauteilen.
👉Die Hauptanwendung von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
Vorteile und Grenzen von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
Vorteile
▶ Hervorragende elektrische Isolierung
▶ Hohe Härte und Verschleißfestigkeit
▶ Gute chemische und thermische Stabilität
▶ Kostengünstig für viele industrielle Anwendungen
Einschränkungen
▶ Sprödes Verhalten unter Stoß- oder Zugbeanspruchung
▶ Mäßige Wärmeleitfähigkeit im Vergleich zu Aluminiumnitrid
▶ Begrenzte Temperaturwechselbeständigkeit im Vergleich zu Nichtoxidkeramiken
Das Verständnis sowohl der Vorteile als auch der Grenzen ist für die richtige Materialauswahl unerlässlich.
Typische Anwendungen von Aluminiumoxidkeramik
Aluminiumoxidkeramik findet aufgrund ihrer vielseitigen Leistungseigenschaften in vielen Branchen breite Anwendung.
Typische Anwendungsgebiete sind:
▶ Elektrische Isolationskomponenten
▶ Verschleißfeste Industrieteile
▶ Hochtemperaturofenkomponenten
▶ Keramische Pumpen- und Ventilkomponenten
In jedem Fall wird Aluminiumoxidkeramik gewählt, weil sie ein praktisches Gleichgewicht zwischen Leistung, Zuverlässigkeit und Kosten bietet.
Aluminiumoxidkeramik im Vergleich zu anderen technischen Keramiken
Bei der Auswahl keramischer Werkstoffe wird Aluminiumoxid häufig mit Alternativen wie Zirkonoxid, Aluminiumnitrid und Siliziumnitrid verglichen.
▶ Aluminiumoxid vs. Zirkonoxid: Aluminiumoxid bietet eine bessere Dimensionsstabilität bei hohen Temperaturen, Zirkonoxid hingegen eine höhere Bruchzähigkeit.
▶ Aluminiumoxid vs. Aluminiumnitrid: Aluminiumoxid bietet eine überlegene Isolierung zu geringeren Kosten, während Aluminiumnitrid sich durch seine Wärmeleitfähigkeit auszeichnet.
▶ Aluminiumoxid vs. Siliziumnitrid: Aluminiumoxid ist wirtschaftlicher, Siliziumnitrid bietet hingegen eine bessere Temperaturwechselbeständigkeit und mechanische Zähigkeit.
Wann Aluminiumoxidkeramik nicht die beste Wahl ist
Obwohl Aluminiumoxidkeramik weit verbreitet ist, eignet sie sich nicht für jede Anwendung.
Alternative Materialien können dann bevorzugt werden, wenn:
▶ Es ist eine extrem hohe Wärmeleitfähigkeit erforderlich
▶ Es herrschen extreme thermische Schockbedingungen.
▶ Außergewöhnliche Bruchzähigkeit ist entscheidend
In solchen Fällen können andere technische Keramiken eine bessere Langzeitleistung bieten.
Aluminiumoxid-Keramikkomponenten bei Mascera
Bei Mascera werden Aluminiumoxid-Keramikkomponenten typischerweise in Reinheitsgraden hergestellt, die üblicherweise für industrielle und elektronische Anwendungen spezifiziert werden.
Die Materialauswahl basiert auf Kundenzeichnungen, funktionalen Anforderungen und der Herstellbarkeit, um eine zuverlässige Leistung in realen Anwendungen zu gewährleisten.
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu Aluminiumoxidkeramik
Ist Aluminiumoxidkeramik ein elektrischer Isolator?
Ja, Aluminiumoxidkeramik ist ein ausgezeichneter elektrischer Isolator und wird in elektrischen und elektronischen Bauteilen häufig verwendet.
Ist Aluminiumoxidkeramik spröde?
Wie die meisten Keramiken ist auch Aluminiumoxid spröde und erfordert daher geeignete Konstruktionsüberlegungen, um ein Versagen durch Stöße oder Zugkräfte zu vermeiden.
Was ist die maximale Betriebstemperatur von Aluminiumoxidkeramik?
Die maximale Betriebstemperatur hängt von der Reinheit und den Anwendungsbedingungen ab, ist aber im Allgemeinen für industrielle Hochtemperaturumgebungen geeignet.
Lässt sich Aluminiumoxidkeramik bearbeiten?
Aluminiumoxidkeramik kann mit speziellen Diamantwerkzeugen bearbeitet werden, typischerweise nach dem Sintern für Präzisionsanwendungen.
Aluminiumoxid-Keramikprodukte: Um den praktischen Anforderungen von Konstruktion und Fertigung gerecht zu werden, bietet Mascera ein umfassendes Sortiment an Aluminiumoxid-Keramikprodukten, darunter Standardformen und kundenspezifisch gefertigte Komponenten. Unser Produktportfolio umfasst Substrate, Rohre, Stäbe, Platten und Verschleißteile für elektronische, thermische und mechanische Anwendungen.
🔗 Entdecken Sie unser Sortiment an Aluminiumoxid-Keramikprodukten.




